Medilife Doctor at home in Dubai
Prenatal testing at home in Dubai 24/7
Experience convenient and reliable prenatal testing at your home in dubai. Ensure your peace of mind with professional, safe and accurate screening services tailored to your needs.
What is prenatal testing?
Prenatal testing / Antenatal tests / Screening Tests in pregnancy, refers to medical tests performed during pregnancy to check the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. These tests can help identify potential health issues, genetic conditions, or congenital abnormalities.
What are the types of Prenatal tests?
- Screening Tests: These are non-invasive tests that estimate the risk of certain conditions. Common screening tests include blood tests, ultrasound scans, and the combined first-trimester screening, which assesses the risk of chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome.
2. Diagnostic Tests: These are more invasive and provide a definite diagnosis of specific conditions. Examples include:
- Amniocentesis: A sample of amniotic fluid is taken from the uterus to test for genetic abnormalities.
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): A small sample of cells from the placenta is tested for chromosomal conditions.
Both types of tests help expectant parents to make informed decisions about their pregnancy and plan for any special care that might be needed.
Who should consider getting prenatal tests during pregnancy?
Prenatal testing is generally recommended for the following groups:
- All Pregnant Women
- Pregnant Women Over age 35
- Family History of Genetic Disorders
- Previous Pregnancy Issues
- Abnormal Screening Results
- Certain Medical Conditions like Diabetes
- Exposure to Harmful Substances
It’s always important for expectant mothers to discuss prenatal testing options with their healthcare provider to understand the risks, benefits, and limitations.
Why should you take prenatal tests ?
The prenatal tests are safe and provide early insights into the health of the pregnancy and any potential risks associated with mother and baby, allowing for early intervention and preparation if needed.
Are prenatal tests safe?
Yes, most prenatal tests, are generally safe and usually involves testing your blood, and other non invasive tests like ultrasounds.
However, when indicated in case of conditions with high risk pregnancy invasive tests carry a small risk of miscarriage.
What are the tests which can be done in first trimester of pregnancy?
In the first trimester of pregnancy, several prenatal tests can help assess the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. These include:
Blood Tests
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checks for anaemia and infections.
- Blood Type and Rh Factor: Determines if there’s an Rh incompatibility, which might require special care.
- Infectious Disease Screening: Tests for diseases like HIV, hepatitis B, syphilis, and rubella immunity.
Ultrasound
- Dating Ultrasound (6-10 weeks): Confirms pregnancy, checks gestational age, and determines the expected due date.
- Nuchal Translucency (NT) Scan (11-14 weeks): Measures the fluid at the back of the fetus’s neck to assess the risk of chromosomal conditions such as Down syndrome.
Genetic Screening
- Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) Test (as early as 10 weeks): Analyses fetal DNA in the mother’s blood to assess the risk for chromosomal conditions like trisomies 21, 18, and 13.
- Combined First-Trimester Screening (cFTS): Combines blood tests (PAPP-A and free beta-hCG) and the NT scan to assess risk for certain genetic conditions.
Urine Test
- Urine Culture: Screens for asymptomatic infections, which are important to treat during pregnancy.
What are the tests which can be done in second trimester of pregnancy?
During the second trimester, typically from 13 weeks to 26 weeks of pregnancy, prenatal tests may be offered to monitor both maternal health and fetal development.
Ultrasound (Anomaly Scan): around 18-22 weeks.
- This detailed ultrasound checks the baby’s organs, limbs, and overall anatomy. It can help identify structural abnormalities and assess fetal growth, the placenta, and amniotic fluid levels.
Maternal Serum Screenings: between 15-20 weeks
- Quad Screen: Measures levels of four substances in the mother’s blood (AFP, hCG, estriol, and inhibin A). It assesses the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and neural tube defects.
- Triple Screen: Similar to the Quad but without inhibin A. (AFP, hCG, estriol)
Glucose Screening Test (for Gestational Diabetes): Usually done between 24-28 weeks.
- To check for gestational diabetes, which can develop in pregnancy and may require dietary changes or medication to manage.
Amniocentesis (if recommended): Typically performed between 15-20 weeks if indicated.
- A diagnostic test that involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid to check for genetic disorders or neural tube defects. usually offered to women with higher risk factors or abnormal screening results.
Fetal Echocardiography: Around 18-24 weeks if needed.
- A detailed ultrasound of the fetal heart, usually recommended if there’s a family history of heart defects, or if anomalies were detected in the initial ultrasound.
Routine Maternal Blood and Urine Tests
- Blood Tests: Check for anaemia, infection, and Rh antibodies.
- Urine Tests: Screen for urinary tract infections, protein levels, and glucose, which are indicators for conditions like preeclampsia and gestational diabetes.
These tests are optional and vary based on individual health needs and risk factors.
Medilife Doctor at home in Dubai
Double marker test in Pregnancy
Ensure peace of mind with our reliable Double Marker Test at your home in Dubai – early detection of chromosomal anomalies for a healthier, worry free pregnancy”
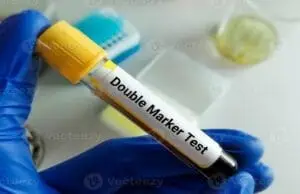
What is Double Marker Test in pregnancy?
The Double Marker Test also known as ‘Maternal serum screening’, is a blood test conducted during pregnancy, usually between 10-14 weeks. It screens for chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) and Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18) by measuring levels of two markers:
- Free Beta HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): A hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy.
- PAPP-A (Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein-A): A protein also produced by the placenta.
It’s important to remember that the result only tells you whether there’s an increased risk of trisomy. It doesn’t definitively determine whether your baby has any abnormalities.
Medilife Doctor at home in Dubai
NIPT Test at Home in Dubai-
“Ensure your baby’s well-being with our Non-Invasive Prenatal Test(NIPT)– a safe, reliable, and early detection for a healthier pregnancy. Trust in cutting-edge screening for peace of mind.”

What is "NIPT Test" in pregnancy?
The NIPT (Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing) is a blood test conducted during pregnancy that screens for certain genetic conditions in the fetus, particularly chromosomal abnormalities.
During pregnancy, a small amount of fetal DNA circulates in the mother’s blood. NIPT analyses this fetal DNA for any abnormalities in chromosome numbers.
- NIPT primarily screens for common chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13).
It can typically be performed as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy, making it one of the earlier screening options available.
Benefits: NIPT is non-invasive, meaning it poses no risk to the fetus, unlike invasive diagnostic tests. It’s also relatively simple and can be done with a standard blood draw.
Recommendations for NIPT:
- Women with higher-risk pregnancies, such as those over age 35,
- those with a family history of genetic disorders, or those with abnormal ultrasound findings, though it’s available to all pregnant women.
IV Therapy FAQs
Common inquiries regarding Prenatal testing
Prenatal testing includes various tests conducted during pregnancy to check the health of the fetus and detect any potential genetic disorders or health issues.
Common types include blood tests (like the first-trimester screening and quad screen), ultrasound scans, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Typically, the first prenatal visit occurs around 8 weeks of pregnancy, where initial screenings and blood tests are conducted.
Most prenatal tests, such as ultrasounds and blood tests, are safe. However, invasive tests like amniocentesis carry a small risk of miscarriage.
NIPT is a blood test that analyses small fragments of fetal DNA circulating in a pregnant woman’s blood to assess the risk of certain genetic conditions, like Down syndrome.
All Pregnant women can take the prenatal test, to check the health of the baby and monitor for a safe and healthy pregnancy .
All high risk pregnancy women should undergo the genetic screening tests to know the health of baby.
A high-risk pregnancy is when the health of the mother or baby is more prone to complications.This can be due to factors like:
- High Maternal Age (<17 or >35 )
- Pre-existing conditions like Diabetes, High Blood Pressure,Heart or Kidney Diseases, or Obesity
- Pregnancy complications like Preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and multiple pregnancies.
- Lifestyle factors like Smoking, alcohol, or drug abuse
- History Of Complicated Pregnancy
High risk pregnancies require close monitoring and specialized care to manage potential issues effectively.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, a range of tests is recommended to monitor the health of both mother and baby, these includes:
- Complete Blood Count
- Blood Group and Rh Factor
- Tests for HIV, Hepatitis B, Syphilis, and rubella immunity.
- Blood Sugar Test
- urine test
- Genetic Screening Test: Non Invasive Prenatal Test(NIPT)
- Ultrasound
In second trimester of pregnancy (weeks 13 -26), tests are recommended to monitor health of both mother and baby:
- Routine blood Test: CBC
- Urine test
- Glucose Screening test
- Genetic Screening: Triple Screen, Quad Screen
Prenatal testing offers several benefits for pregnant mothers and healthcare providers:
- Early Detection of Genetic Disorders
- Monitoring Fetal Health
- Parental Preparation
- Reducing Risks: prenatal screening helps to identify pregnancy complications like preeclampsia, anemia or gestational diabetes, which can be managed early for better outcomes for both mother and baby
- Peace Of Mind: Knowing that baby is developing normally reduces anxiety and helps parents to feel more secure during pregnancy.
- Informed Choices
Quad Screen is prenatal test that measures 4 substances (HCG, Estriol, AFP, Inhibin A) in a pregnant woman’s blood to assess the risk of certain birth defects, like Down’s syndrome, Edward syndrome, neural tube defects.
Triple screen is a blood test performed in pregnancy which measures the level of three substances : HCG, Estriol, AFP in the blood, to assess the risk of certain fetal conditions like Down’s syndrome, Edward syndrome and neural tube defects.
The screening tests to detect Down’s syndrome are:
- Double Marker test
- NIPT Test
- Triple Screen
- Quad Screen/Quadruple Test
